Demonstrates basic operations with the Redshift renderer in Cinema 4D.
About
With S26 the Redshift render engine has been integrated with Cinema 4D. While the render engine has already previously been available to Cinema 4D users, it was then a plugin and therefor not part of the public Cinema 4D SDK. With the integration come also architectural changes as for example the unification of camera and light types and a unified nodes model.
Current Limitations
In the current form of Redshift integration there are no Redshift specific frameworks yet exposed. But the core features of Redshift can be accessed through the classic and Nodes API. Currently missing from the public API are also the Redshift render engine ID and the Redshift node space ID for node materials. They must be provided manually in third party code at the moment as demonstrated by the examples here.
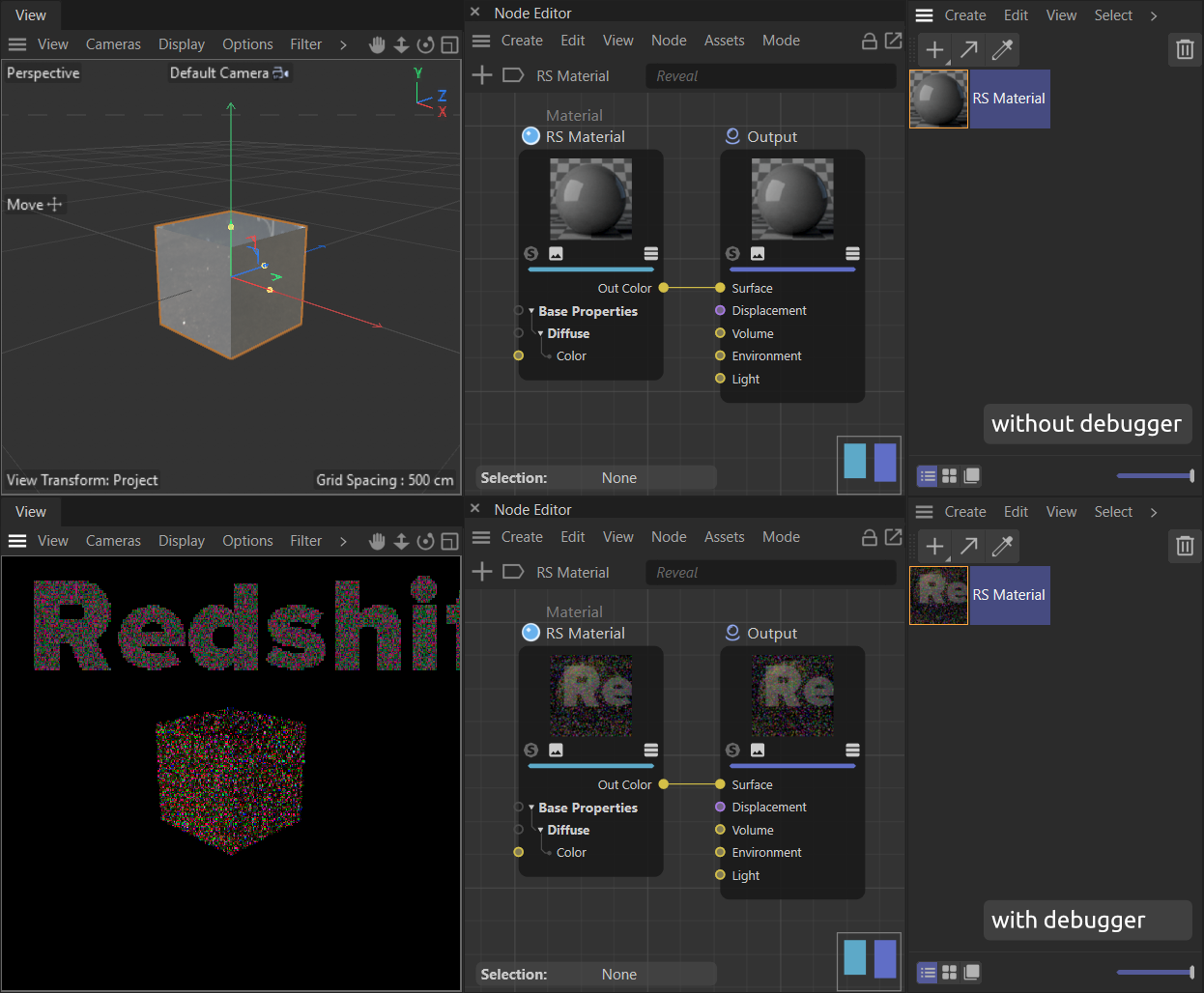
Redshift has also an anti-tampering mechanism which ensures Redshift is being run with a valid license. This mechanism triggers when a debugger, as for example provided by Visual Studio and XCode, is attached to Cinema 4D. The anti-tampering mechanism then obfuscates the rendering output of Redshift as shown in Figure I. Plugins making use of Redshift can still be debugged as any other plugin, but to see the final output of a plugin which generates for example a Redshift node material setup, the plugin must be compiled and loaded by a normal instance of the Cinema 4D application without a debugger attached.
Examples
Set Render Engine to Redshift
Sets the render engine of the active render data of a document to Redshift.
Also assures that the required Redshift video post node is present in the render data. This example requires defining the Redshift renderer plugin ID as shown here, as the ID is currently not exposed in the SDK.
{
if (rdata == nullptr)
return maxon::UnexpectedError(
{
if (rdata == nullptr)
return nullptr;
while (videoPost)
{
return videoPost;
}
return nullptr;
};
{
if (!redshiftVideoPost)
return maxon::OutOfMemoryError(
}
}
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:48
void SetInt32(Int32 id, Int32 l)
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:587
Definition: c4d_basedocument.h:497
const BaseContainer * GetDataInstance() const
Definition: c4d_baselist.h:2530
Definition: c4d_videopost.h:24
static BaseVideoPost * Alloc(Int32 type)
BaseVideoPost * GetNext() const
Definition: c4d_videopost.h:56
Bool IsInstanceOf(Int32 id) const
Definition: c4d_baselist.h:1562
Definition: c4d_basedocument.h:143
void InsertVideoPost(BaseVideoPost *pvp, BaseVideoPost *pred=nullptr)
BaseVideoPost * GetFirstVideoPost()
@ RDATA_RENDERENGINE
Definition: drendersettings.h:39
maxon::Int32 Int32
Definition: ge_sys_math.h:56
return OK
Definition: apibase.h:2735
#define MAXON_SOURCE_LOCATION
Definition: memoryallocationbase.h:67
@ NEWOBJ
A new object, material, tag, or other classic API node instance has been inserted into the document....
@ CHANGE
Any change to an object, including hierarchy modifications, modification in positioning,...
#define VPrsrenderer
Videopost plugin 'Redshift'. @PublicExposure.
Definition: c4d_videopostdata.h:250
const char * doc
Definition: pyerrors.h:226
#define iferr_scope
Definition: resultbase.h:1389
Render a Document with Redshift
Renders the current frame in a document with the Redshift render engine into a bitmap.
The bitmap is displayed with the Picture Viewer after the rendering has finished. Uses the function RenderDocument to render the document and the example snippet Set Render Engine to Redshift to set the render engine of the passed document.
{
if (rdata == nullptr)
return maxon::UnexpectedError(
}
RENDERRESULT RenderDocument(BaseDocument *doc, const BaseContainer &rdata, ProgressHook *prog, void *private_data, BaseBitmap *bmp, RENDERFLAGS renderflags, BaseThread *th, WriteProgressHook *wprog=nullptr, void *data=nullptr)
Bool ShowBitmap(const Filename &fn)
BaseBitmap * AddChannel(Bool internal, Bool straight)
static BaseBitmap * Alloc()
Int32 GetInt32(Int32 id, Int32 preset=0) const
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:348
Definition: c4d_basebitmap.h:990
static void Free(MultipassBitmap *&bm)
@ RDATA_XRES
Definition: drendersettings.h:152
@ RDATA_YRES
Definition: drendersettings.h:153
int32_t Int32
32 bit signed integer datatype.
Definition: apibase.h:190
@ EXTERNAL
External render.
#define iferr_return
Definition: resultbase.h:1524
Create a Redshift Camera
Instantiates a Redshift camera and inserts it into a document.
Also modifies the projection mode, the near clipping plane and the transform of the new camera to demonstrate setting up a camera in more detail.
{
if (redshiftCamera == nullptr)
redshiftCamera->
SetMg(transform);
doc->InsertObject(redshiftCamera,
nullptr,
nullptr);
if (!renderBaseDraw)
if (!convertStdCamera)
const Float stdCameraApperatureValue = 50.0;
if (!convertRsCamera)
return maxon::OutOfMemoryError(
convertStdCamera->
SetName(
"Conversion Redshift->Standard"_s);
convertRsCamera->
SetName(
"Conversion Standard->Redshift"_s);
doc->InsertObject(convertRsCamera,
nullptr,
nullptr);
doc->InsertObject(convertStdCamera,
nullptr,
nullptr);
}
Float GetFloat(Int32 id, Float preset=0.0) const
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:380
void SetFloat(Int32 id, Float r)
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:615
void SetBool(Int32 id, Bool b)
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:580
Definition: c4d_basedraw.h:755
void SetSceneCamera(BaseObject *op, Bool animate=false)
Definition: c4d_basedraw.h:832
void SetName(const maxon::String &name, Bool setDirty=true)
Definition: c4d_baselist.h:2550
Definition: c4d_baseobject.h:248
void SetMg(const Matrix &m)
Definition: c4d_baseobject.h:516
static BaseObject * Alloc(Int32 type)
Bool SetParameter(const DescID &id, const GeData &t_data, DESCFLAGS_SET flags)
Definition: c4d_gedata.h:83
maxon::Vec3< maxon::Float64, 1 > Vector
Definition: ge_math.h:141
maxon::Float Float
Definition: ge_sys_math.h:62
constexpr MAXON_ATTRIBUTE_FORCE_INLINE Float32 DegToRad(Float32 r)
Converts float value from degrees to radians.
Definition: apibasemath.h:474
#define Orscamera
New Camera Object (Redshift)
Definition: ge_prepass.h:1047
#define Ocamera
Camera - CameraObject.
Definition: ge_prepass.h:1046
#define ConstDescID(...)
Definition: lib_description.h:594
@ CAMERAOBJECT_APERTURE
Definition: ocamera.h:42
@ RSCAMERAOBJECT_PROJECTION_ORTHOGRAPHIC
Definition: orscamera.h:229
@ RSCAMERAOBJECT_NEAR_CLIPPING_ENABLE
Definition: orscamera.h:18
@ RSCAMERAOBJECT_APERTURE
Definition: orscamera.h:46
@ RSCAMERAOBJECT_PROJECTION
Definition: orscamera.h:10
@ RSCAMERAOBJECT_NEAR_CLIPPING
Definition: orscamera.h:17
Represents a level within a DescID.
Definition: lib_description.h:298
Create a Redshift Light Object
Instantiates a Redshift light object and inserts it into a document.
Also modifies the light type and shape, the color and intensity and the transform of the new light object to demonstrate setting up a light object in more detail. Finally, adds a target tag to the light object to orient towards a dummy geometry created alongside with this example.
{
if (redshiftLight == nullptr)
redshiftLight->
SetMg(transform);
doc->InsertObject(redshiftLight,
nullptr,
nullptr);
if (cubeObject == nullptr)
doc->InsertObject(cubeObject,
nullptr,
nullptr);
if (targetTag == nullptr)
}
void SetLink(Int32 id, const C4DAtomGoal *link)
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:686
void SetVector(Int32 id, const Vector &v)
Definition: c4d_basecontainer.h:637
BaseTag * MakeTag(Int32 type, BaseTag *pred=nullptr)
Definition: c4d_basetag.h:52
#define Orslight
Redshift light.
Definition: ge_prepass.h:1045
#define Ocube
Cube.
Definition: ge_prepass.h:1119
#define Ttargetexpression
Target expression.
Definition: ge_prepass.h:1425
@ REDSHIFT_LIGHT_AREA_GEOMETRY_DISC
Definition: orslight.h:200
@ REDSHIFT_LIGHT_PHYSICAL_COLOR
Definition: orslight.h:47
@ REDSHIFT_LIGHT_TYPE
Definition: orslight.h:9
@ REDSHIFT_LIGHT_TYPE_PHYSICAL_AREA
Definition: orslight.h:189
@ REDSHIFT_LIGHT_PHYSICAL_INTENSITY
Definition: orslight.h:51
@ REDSHIFT_LIGHT_PHYSICAL_AREA_GEOMETRY
Definition: orslight.h:57
@ TARGETEXPRESSIONTAG_LINK
Definition: ttargetexpression.h:6
Create a Redshift Material
Creates a Redshift node material, modifies its node graph and inserts the material into a document.
The example adds two Texture nodes, a Color Mix node, and a Maxon Noise node to the node graph of the material and creates connections between these nodes. The two texture nodes are setup to reference texture assets delivered with Cinema 4D. See Asset API for more information on the asset system of Cinema 4D which is used here.
{
Bool didInsertMaterial =
false;
{
"Could not unroll or finalize undo stack upon error handling."_s };
"Critical error while aggregating errors."_s };
if (
doc && material && didInsertMaterial)
{
if (!isUndoError)
{
isUndoError = !
doc->EndUndo();
}
if (isUndoError)
{
iferr (aggError.AddError(maxon::Error(err)))
return critError;
iferr (aggError.AddError(undoError))
return critError;
return aggError;
}
}
return maxon::Error(err);
};
return maxon::IllegalStateError(
const maxon::Url rustTextureUrl {
"asset:///file_edb3eb584c0d905c"_s };
const maxon::Url sketchTextureUrl {
"asset:///file_3b194acc5a745a2c"_s };
if (!material)
const maxon::LiteralId redshiftId(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.class.nodespace");
doc->InsertMaterial(material);
didInsertMaterial = true;
return maxon::IllegalStateError(
const maxon::Id outputNodeTypeId(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.node.output");
const maxon::Id materialNodeTypeId(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.nodes.core.standardmaterial");
const maxon::Id colormixNodeTypeId(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.nodes.core.rscolormix");
const maxon::Id noiseNodeTypeId(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.nodes.core.maxonnoise");
const maxon::Id textureNodeTypeId(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.nodes.core.texturesampler");
{
maxon::Id(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.nodes.core.texturesampler.tex0")).FindChild(
maxon::Id(
"com.redshift3d.redshift4c4d.nodes.core.texturesampler.tex0")).FindChild(
}
Bool GeIsMainThreadAndNoDrawThread()
static BaseMaterial * Alloc(Int32 type)
void Remove()
Definition: c4d_baselist.h:2067
Definition: c4d_basematerial.h:391
maxon::Result< const maxon::nodes::NodesGraphModelRef & > GetGraph(const maxon::Id &spaceId) const
Definition: c4d_basematerial.h:475
maxon::Result< void > CreateEmptyGraph(const maxon::Id &spaceId)
Definition: c4d_basematerial.h:496
Definition: errorbase.h:126
Result< typename SFINAEHelper< GraphNode, BASE >::type > GetOutputs() const
Definition: graph.h:1236
Result< typename SFINAEHelper< GraphNode, BASE >::type > GetInputs() const
Definition: graph.h:1225
Result< void > Connect(const GraphNode &target, Wires modes=WIRE_MODE::CONNECT_DEFAULT, Bool reverse=false) const
Definition: graph.h:1534
Result< Bool > SetPortValue(T &&value) const
Definition: graph.h:1832
Result< void > Commit(const DataDictionary &userData=GetPtrSizedZeroRef< DataDictionary >(), Bool validate=true)
Definition: apibaseid.h:243
Definition: apibaseid.h:28
void * userData
Definition: fileobject.h:20
maxon::Bool Bool
Definition: ge_sys_math.h:51
#define Mmaterial
Standard material.
Definition: ge_prepass.h:1008
@ NOISE_WAVY_TURB
Wavy turbulence.
Definition: lib_noise.h:60
#define iferr(...)
Definition: errorbase.h:388
@ DELETEOBJ
An object, node, tag, or other classic API node instance is about to be deleted. Must to be called be...
@ ADD
Add an undo entry, but don't start a new undo.
#define iferr_scope_handler
Definition: resultbase.h:1407